Creatine Explained: What It Is, How It Works, and Why You Should Consider Taking It
I still remember the first time I heard about creatine. I was 19, scrolling through a fitness forum, and every other post was some guy swearing it was the secret to his muscle growth. I was skeptical. Could a powder you scoop into water really make that much of a difference?
Fast forward over 10 years, and I can confidently say creatine has been one of the simplest — and most effective — supplements I’ve ever used. But not for the reasons most ads try to sell you on.
What Is Creatine?
Forget the overcomplicated science talk for a second. Creatine is basically stored energy for your muscles. When you lift weights, sprint, or do anything explosive, your muscles burn through energy quickly. Creatine gives them a little backup battery so you can push harder for a few more reps or a little more weight. Over time, that small edge adds up to more strength and muscle.
How Does It Work?
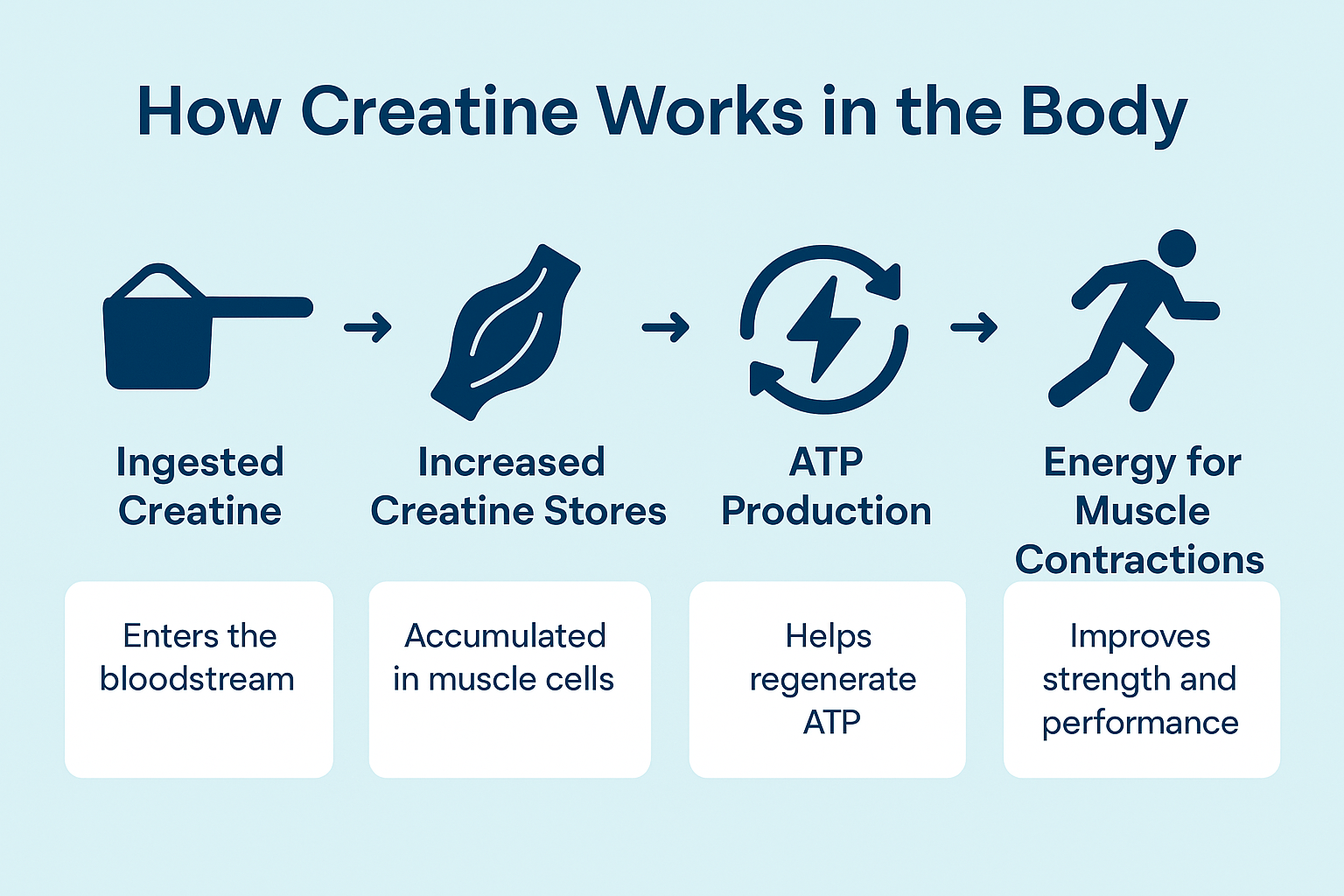
It helps replenish your body’s supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of your cells. During intense physical activity, your body burns through ATP quickly. This supplement donates a phosphate group to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) to regenerate ATP, allowing you to sustain high energy output for longer periods.
This is why it’s so beneficial for:
- Strength training
- Sprinting
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT)
- Sports requiring explosive movements (football, basketball, etc.)
Should You Take It?
Yes, and not just if you’re lifting weights. This supplement is beneficial for almost everyone because of its wide range of effects on both body and brain. You don’t have to be a daily gym rat to enjoy the benefits.
Here are the Top 5 Reasons to Use It (Even if You Don’t Work Out Every Day):
- Improves Brain Functionality
- Studies show it enhances memory, reaction time, and cognitive performance.
- Especially helpful during mental fatigue or sleep deprivation.
- Supports Muscle Health as You Age
- Prevents age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia).
- Promotes better mobility and overall physical function in older adults.
- Boosts Cellular Hydration and Muscle Fullness
- Draws water into muscle cells, increasing volume and improving nutrient delivery.
- Speeds Recovery
- Reduces inflammation and muscle soreness after workouts.
- Supports Overall Health
- Linked to better heart health, improved glucose tolerance, and reduced fatigue in chronic conditions.
Can Creatine Help You Lose Weight?
Yes—though it’s not a fat burner in the traditional sense, creatine can absolutely support a weight loss journey in several powerful ways.
🔥 How It Supports Fat Loss:
- Increases Lean Muscle Mass
More muscle = higher resting metabolic rate. Creatine helps build and preserve lean muscle, which means your body burns more calories even at rest. - Improves Workout Intensity
It allows you to train harder and longer, meaning more calories burned during exercise. Whether you’re lifting weights or doing cardio, you’ll likely push further with creatine in your system. - Reduces Muscle Breakdown
During a calorie deficit, your body may break down muscle for energy. Creatine helps protect that muscle, ensuring the weight you lose is more likely to be fat and not lean mass. - May Help Reduce Fatigue
It can improve energy and reduce tiredness, making it easier to stay consistent with workouts and daily activity—crucial during a cut.
⚠️ What About the Scale?
- You might see a slight increase in weight at first due to water retention inside your muscle cells—not fat gain. This is a good thing and often temporary.
- Over time, many users see better body composition: more muscle, less fat.
💡 Pro Tip: Don’t let the scale trick you. Focus on how you look, feel, and perform rather than just numbers. Creatine can help you get leaner, even if the scale doesn’t budge right away.
Myths: Debunked
- Myth: It’s a steroid.
- Fact: It’s not. This compound is a natural substance found in the body and in foods.
- Myth: It causes kidney damage.
- Fact: No credible research shows harm to healthy kidneys. It’s safe when taken in recommended doses. [Study]
- Myth: You need to “cycle” it.
- Fact: There’s no need to cycle. Long-term use is safe and effective.
- Myth: It causes water retention and bloating.
- Fact: It pulls water into muscle cells, not under the skin, so it doesn’t cause bloating for most people.
The Most Researched Supplement
Over 1,000 studies have evaluated its effects on performance, health, and safety. It’s considered the most researched supplement on the market, with an excellent safety profile. [PubMed Review]
Types: Monohydrate vs. HCL
Here’s a quick comparison of the two most common types:
| Feature | Creatine Monohydrate | Creatine HCL |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption Rate | Moderate | High |
| Dosage Required | 3-5g per day | 1-2g per day |
| Solubility | Less soluble in water | Highly soluble |
| Cost | Budget-friendly | More expensive |
| Research Backing | Extensive | Limited but promising |
| Bloating Risk | Slight (rare) | Minimal |
Which One Should You Choose?
- Choose Monohydrate if:
- You want the most studied, most affordable option.
- You don’t mind mixing it in a shaker bottle.
- Choose HCL if:
- You’ve experienced bloating or digestive issues with monohydrate.
- You prefer a smaller serving size and faster absorption.
Which Type Actually Works
You’ve probably seen “micronized,” “buffered,” and “liquid” creatine at the store. Honestly? Plain creatine monohydrate works best for 99% of people. It’s cheap, proven by decades of research, and it’s what I still use today.
My Top Creatine Picks
If you’re looking for creatine, these are the brands I recommend based on personal experience, quality, and price.
(Some of the links below are affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you — it helps support ACG Fitness, and I appreciate it!)
| Brand | Type | Price Range | My Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optimum Nutrition Creatine Monohydrate (Amazon Link) | Powder | $20–$25 for 60 servings | Mixes well, trusted brand, no fillers. |
| MyProtein Creatine Monohydrate (MyProtein Link) | Powder | $15–$20 for 50 servings | Affordable, often on sale, clean formula. |
| Bulk Supplements Creatine Monohydrate (Amazon Link) | Powder | $25–$30 for 100 servings | Huge bag, great value, no frills. |
| Kaged Creatine HCl (Amazon Link) | Powder | $25–$35 for 75 servings | Smaller serving size, good if you hate powders. |
For most people, monohydrate is the go-to. It’s affordable, effective, and has decades of research to back it up.
Get 40% off MyProtein Creatine Monohydrate with code MYPVIP40 at checkout. Click here to shop now.
Other Forms: Pills, Gummies, and More
While powder is the most common and effective form, creatine also comes in other formats:
- Pills
- Pros: Convenient, travel-friendly, no need to mix.
- Cons: Often requires multiple pills to reach the effective dose.
- Gummies
- Pros: Tasty and fun to take.
- Cons: May contain added sugars, lower dose per serving, and higher cost.
- Liquid Creatine
- Pros: Easy to use on-the-go.
- Cons: Some versions have lower stability or effectiveness.
Despite these options, powder form remains the most effective and economical choice. It mixes well with protein shakes or juice and allows precise control over dosage.
How to Take It Properly

- Loading Phase (Optional):
- 20g/day for 5-7 days (split into 4 doses)
- Maintenance Phase:
- 3-5g/day for monohydrate
- 1-2g/day for HCL
- When to Take It:
- Anytime works, but post-workout with carbs/protein may enhance uptake.
- Drink Water:
- Stay hydrated, as it increases water retention in muscles.
- Bonus Tip:
- This supplement is extremely convenient to mix with your daily protein shake—just one scoop and you’re good to go.
- 👉 Check out our blog post on the Best Pre-Made Protein Shakes
Creatine and Diet: What You Should Know

While taking creatine is effective on its own, combining it with the right nutrition can further enhance results. Here’s how your diet plays a role:
- Carbs Enhance Absorption
Pairing creatine with carbohydrates (like a banana or a post-workout shake) helps spike insulin levels, which promotes better absorption into muscle cells. - Hydration Is Key
Since creatine pulls water into your muscles, staying well-hydrated is critical. Dehydration may reduce its effectiveness and lead to cramps. - Best Foods That Naturally Contain Creatine
- Red meat
- Chicken
- Salmon
- Eggs
- Tuna
These foods contain small amounts of creatine—helpful, but not enough to match supplement doses.
- Vegetarians and Vegans Benefit Even More
Since plant-based diets contain little to no creatine, those following vegan or vegetarian lifestyles often see greater performance and cognitive benefits when they supplement.
💡 Pro Tips:
Pair creatine with a protein + carb combo post-workout for the best results.
If you’re eating a low-meat or plant-based diet, creatine supplementation is practically essential to meet optimal levels.
Is It for Everyone?
While it’s safe for most people, here are a few cases where you should consult a doctor before taking it:
- You have pre-existing kidney disease
- You’re on diuretics or medications affecting water balance
- You’re pregnant or breastfeeding
Is Creatine Safe for Diabetics?
Yes — for most people with diabetes, creatine is considered safe when taken at recommended doses. In fact, some studies suggest that creatine may improve glucose tolerance and even enhance insulin sensitivity, especially when combined with exercise.
✅ Potential Benefits for Diabetics:
- May help regulate blood sugar levels when paired with resistance training.
- Can improve muscle function and reduce fatigue, which is helpful since diabetes can affect energy and physical performance.
- Supports brain and nerve health, areas often impacted by long-term high blood sugar.
⚠️ Precautions:
- Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement, especially if you’re on medications like insulin or metformin.
- Stay well-hydrated to avoid any added kidney strain.
- Avoid mega-dosing; stick to the standard 3-5g/day (monohydrate) or 1-2g/day (HCL).
Creatine FAQs

Q: Can I take it on rest days?
A: Yes! In fact, consistent daily intake is important for maintaining elevated levels.
Q: Is it safe for teens?
A: Generally yes, especially for active teens, but it’s best to check with a pediatrician.
Q: Can it cause insomnia or affect sleep?
A: No strong evidence suggests it disrupts sleep; some report better recovery and sleep quality.
Q: Can I mix it with coffee or tea?
A: Yes! Just be sure to stay hydrated, as caffeine is a mild diuretic.
Final Thoughts
This isn’t just for bodybuilders. It’s a powerful, science-backed supplement that supports strength, recovery, cognitive function, and long-term health. Whether you’re lifting heavy or just want better brain performance, it’s worth considering. It’s the most effective and trusted supplement on the market.
Still on the fence? Start with a small dose of creatine monohydrate and track how you feel. Chances are, you’ll notice increased energy, better workouts, and maybe even a sharper mind.
Have questions or your own experience to share? Drop a comment below or reach out to us on IG @acgfitness!
Stay strong, stay sharp.
This article is brought to you by ACG Fitness. For more science-backed guides and fitness tips, visit our blog or follow us on social media.



2 thoughts on “Creatine 101: The Truth, My Experience, and How to Use It for Real Gains”